Know Your Customers & Outsell by using STP Marketing Model with Coca-Cola

What is STP Marketing Model?
The STP marketing strategy is an approach to effectively and accurately communicate the value of a product to the right target audience. Let’s take a closer look at the model to gain a better understanding.
STP Marketing comes from
- Segmentation (Dividing the target audience)
- Targeting (Defining the target audience)
- Positioning (Establishing the market position of the product)
STP marketing focuses on selecting the most valuable target customer groups for a business. It then develops a tailored Marketing Mix Strategy and Product Positioning Strategy for each segment. By segmenting the target audience, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their customers. Once specific groups of people with similar interests and values are identified, businesses can fine-tune their product offerings to meet each segment’s needs with precision.
This technique helps businesses communicate effectively with their target audiences by emphasizing the product benefits that align with what each group is looking for.
The first step is identifying and segmenting customers based on factors such as interests, perspectives, and other shared characteristics. Once you understand each target group, you can tailor marketing content and campaigns to suit them effectively. Imagine talking to different groups of friends—you would use different language and communication styles depending on the group. The STP Marketing Model works the same way, allowing businesses to engage each segment in a way that resonates with them and captures their attention more effectively.
In-Depth Look at the STP Marketing Model
1. Segmentation – Dividing the Target Audience
The first and most crucial step of the STP Marketing Model is Segmentation, or dividing the target audience. This step is like breaking down a broad market into smaller, clearly defined segments with distinct characteristics.
The key to segmentation is identifying the “value” that each customer group seeks but has not yet received. Then, you position your product or service to fill that gap. But how do we segment our target audience? This process requires in-depth data analysis to truly understand the persona of each customer group.
There are several common methods for segmenting an audience, including:
- Demographics – Age, gender, income level.
- Behavioral – Purchase frequency, usage behavior.
- Psychographics – Lifestyle, beliefs, interests.
- Geographic – Location, environmental factors.
By understanding these factors, businesses can create highly targeted marketing strategies that effectively meet customer needs.
Deep Dive into Segmentation! Techniques for Target Audience Segmentation in the STP Marketing Model for B2C
In B2C marketing, segmentation typically focuses on the characteristics of individual consumers. Examples include:
- Demographics – Segmentation based on age, gender, income, education level, etc.
- Behavioral – Segmentation based on purchase frequency, usage behavior, or lifestyle.
- Psychographics – Segmentation based on interests, beliefs, or values.
- Geographic – Segmentation based on location, environment, or regional consumer behavior.
Example: A cosmetics company may segment its target audience by age, such as teenagers, working professionals, and seniors. Each group has different product needs, communication styles, and marketing channels that resonate with them.
2. Targeting – Defining the Target Audience
After segmenting the market (Segmentation), the next step is Targeting, which involves selecting the most potential customer groups for the business to focus its marketing efforts on.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Target Audience
- Segment Size – The selected market should be large enough compared to the segments identified. If the segmentation is too detailed, the market may become too small, making marketing efforts inefficient.
- Difference Between Segments – Each segment should be distinct to ensure that marketing strategies effectively address the specific needs of each group.
- Budget – The expected profit should outweigh the marketing costs, including advertising expenses, content production, and other marketing-related costs.
- Different Values/Benefits for Each Group – To communicate the value of a product or service effectively, businesses must analyze what each group prioritizes. By presenting a unique selling proposition (USP) that resonates with each segment’s needs, businesses can increase conversion rates and drive more sales.
3. Product Positioning – Establishing a Market Position
Positioning refers to creating a strong and distinct brand image in the minds of customers. In this step, businesses can leverage insights gained from the previous two steps—Segmentation and Targeting—to determine how to effectively communicate the value of their products to different target groups.
For example, if you are targeting price-conscious consumers, your positioning strategy should emphasize affordable yet high-quality lifestyle products that offer great value for money.
Many marketers use a Positioning Map to identify gaps in the market. This map allows businesses to compare two different attributes on a graph, helping them discover opportunities to establish a unique position in the market.
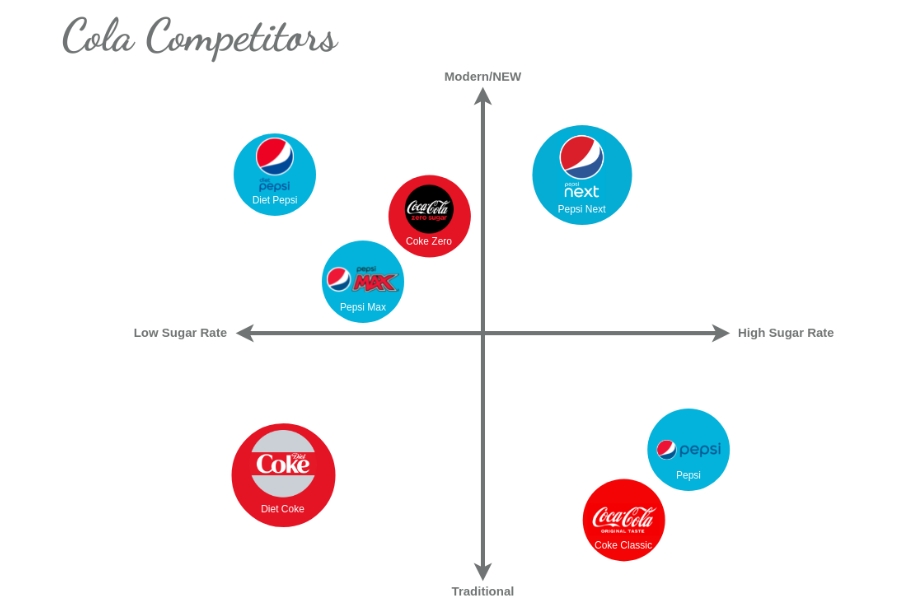
A strong positioning strategy helps your brand stand out in customers’ minds and creates a clear brand image. This can be achieved through the following approaches:
1. Symbolic Aspect – This approach focuses on the image or status that consumers associate with owning a product. Luxury and premium brands often use this strategy to communicate prestige, power, and sophistication.
- Example: A luxury handbag brand may symbolize a higher social status.
2. Functional Aspect – This aspect emphasizes solving problems or inconveniences that your target audience is facing. The key is to identify customer pain points and position your product as the best solution.
- Example: A cosmetics brand may highlight its product’s ability to conceal acne scars, solving a common issue for people with acne concerns.
3. Experiential Aspect – This focuses on the emotions and experiences customers have when using your product. Brands can use this strategy to build an emotional connection with their audience.
- Example: A coffee brand may create a warm and friendly brand image, making customers feel relaxed and at ease every time they enjoy their coffee.
Market research and data analysis
Market research and data analysis help you determine the most effective way to sell your products or services. Conducting customer interviews and gathering feedback allows you to better understand your target audience and decide which market segments to focus on. Analyzing the collected data ensures that your decisions are more thoughtful and precise.
Tracking market trends and data is also crucial. As a business owner, you need to stay informed about industry trends, customer behavior, and competitor strategies. This approach helps refine your targeting methods and brand positioning, ensuring that your brand remains relevant.
In summary, market research and data analysis enable your business to understand customer needs and stay competitive in the market effectively.
Coca-Cola’s Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning Case Study
Coca-Cola uses multiple customer segmentation strategies to reach a diverse target audience.
Firstly, Coca-Cola segments its customers based on geographic location. For example, the company launched the “Share a Coke” campaign in Australia in 2011. This campaign featured the slogan “Share a Coke with” printed on Coca-Cola bottles along with the most popular names in the country. The campaign was a huge success, prompting Coca-Cola to roll it out in various countries, including the United Kingdom, China, and Spain. Of course, Coca-Cola conducted market research to identify the most popular names in each country. A popular name in Australia might work in the UK, but the campaign could fail in China or Spain if it kept printing English names on the bottles. This example demonstrates how Coca-Cola segments customers based on geographic location.
Additionally, Coca-Cola uses various tools to define its target audience. For instance, the company targets health-conscious consumers with products like Coca-Cola Zero and Diet Coca-Cola, while regular products are aimed at the general consumer. The bottle size also plays a significant role in targeting. For example, Coca-Cola targets individuals seeking a quick drink with standard-sized cans, while targeting families with larger 1.5–2-liter bottles.
Finally, Coca-Cola positions itself as a refreshing drink that brings happiness to customers. It is also marketed as a convenient thirst quencher suitable for on-the-go consumption, and a premium carbonated drink ideal for sharing with family and friends.
Sources:
- https://www.symson.com/no/blog/stp-marketing-model
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/stp-marketing-how-market-segmentation-targeting-alexandros-kokolis/
- https://rb.gy/7crgsx
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bc09EcqHTpw
If you are interested in data collection and analysis, feel free to contact us at 099-564-5947, 096-142-9547, or via email [email protected].











